Fuses Tissues Prior to Their Surgically Precise Removal
This hemostatic clamp enables the suture-free removal of unwanted tissues. Unwanted tissues include foreskin from the human penis, skin tags, auricular (ear) tags, and postaxial type-B polydactyly. Polydactyly is the congenital presence of additional digits (fingers or toes) at birth and is a common congenital deformity. Another application for the clamp’s patented technology is veterinary castration.
The accepted “standard of care” for removing extra digits and tags is performing a suture ligature or applying a vascular clamp. These clinical practices are archaic and transferred from veterinary medicine; several complications and ineffective treatment can occur, such as the formation of a “nubbin,” the rupture of a residue (avulsion), bleeding (hemorrhage), infection, and the risk of intense nerve pains (neuroma). Circumcision generally employs surgery, requiring sedation and suturing or cauterization, and has a risk of scar tissue formation and the incomplete or excessive removal of tissue. A better and more precise solution is needed.
Researchers at the University of Florida have developed a hemostatic clamp for removing unwanted tissue with quick, surgical precision. Clinicians can achieve fast and curative removals of skin tags, as well as perform circumcisions, in a suture-free and aseptic fashion. The clamp is sterile, disposable, and offered at an affordable cost. The clamp is for global use, including in humanitarian efforts serving underserved and developing nations.
Application
Hemostatic clamp for the suture-free removal of foreskin, skin tags, auricular tags, and postaxial type-b polydactyly
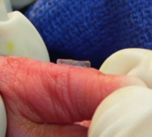
Advantages
- Disposable with a compact design, making the clamp practical for use with smaller tissues and infants
- Fast and curative removal of unwanted tissues, eliminating complications associated with the suture method and providing patients with suture-free, and aesthetically pleasing permanent removal
- Prevents neuroma formation, reducing the need for curative repairs or lifelong discomfort
- The clamp’s locking mechanism maintains pressure and creates a skin tab of the external tissue, enabling quick treatment with minimal scarring
Technology
This clamp employs two opposing clamping surfaces with a locking mechanism. The caretaker places the clamp at the base of the unwanted tissue, locking the device in place. The force generated by the device creates a fusion of the opposing tissue surfaces. Once pressure is applied, a scalpel or a surgical-grade razor is used to excise the tissue. By fusing the tissue, the clamp prevents bleeding at the excision site and encourages the withdrawal of any residual nerves.
